Allergies
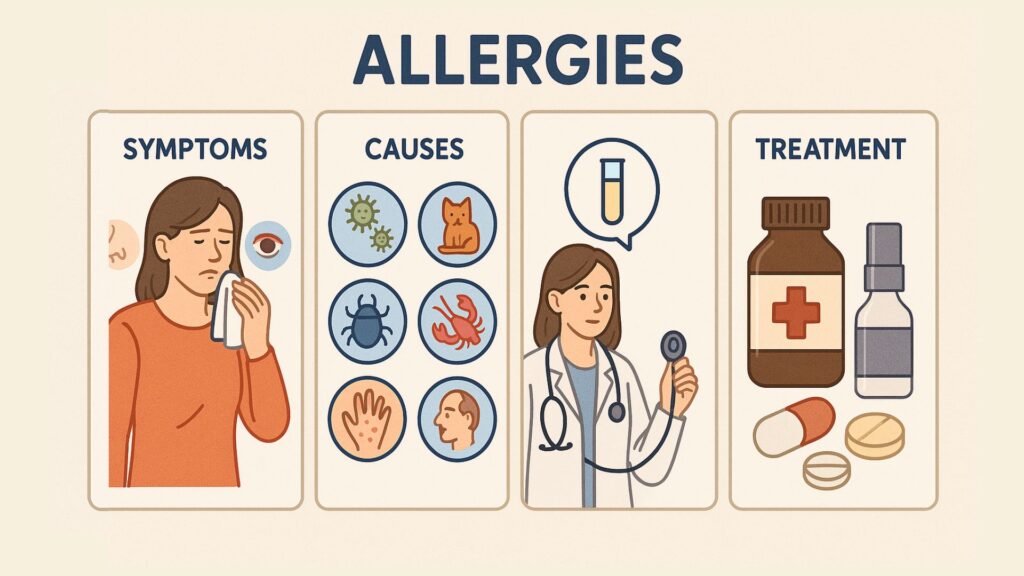
Allergies occur when the immune system overreacts to substances that are usually harmless, called allergens. Here’s a breakdown of different types of allergies, their causes, and common symptoms:
Symptoms
Causes
Treatment
1. Seasonal Allergies (Hay Fever)
- Causes: Pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds.
- Symptoms: Sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy or watery eyes, itchy throat, and sometimes coughing.
2. Dust Mite Allergies
- Causes: Tiny insects living in dust, often found in bedding, carpets, and upholstered furniture.
- Symptoms: Sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy eyes, and coughing.
3. Pet Allergies
- Causes: Proteins found in pet saliva, urine, and dander (tiny flakes of skin).
- Symptoms: Sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy or watery eyes, and sometimes skin reactions like hives.
4. Mold Allergies
- Causes: Mold spores found in damp or humid environments.
- Symptoms: Sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy eyes, coughing, and sometimes skin rashes.
5. Food Allergies
- Causes: Proteins in certain foods like peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, fish, milk, eggs, soy, and wheat.
- Symptoms: Hives, swelling, itching, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis (a life-threatening reaction that includes difficulty breathing and a drop in blood pressure).
6. Drug Allergies
- Causes: Reactions to medications such as antibiotics, aspirin, or certain vaccines.
- Symptoms: Rash, itching, swelling, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis.
7. Insect Sting Allergies
- Causes: Venom from stings of insects like bees, wasps, and hornets.
- Symptoms: Immediate pain, redness, and swelling at the sting site; severe reactions can include difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat, and anaphylaxis.
8. Contact Dermatitis
- Causes: Direct contact with allergens or irritants like certain metals (e.g., nickel), latex, or plants like poison ivy.
- Symptoms: Red, itchy rash, swelling, and sometimes blisters at the contact site.
9. Latex Allergies
- Causes: Proteins found in natural rubber latex used in gloves, balloons, and other products.
- Symptoms: Skin rash, itching, hives, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis.
10. Chemical Allergies
- Causes: Exposure to chemicals found in household cleaning products, personal care products, or industrial substances.
- Symptoms: Skin rashes, itching, and respiratory symptoms like sneezing or coughing.
General Symptoms of Allergies
- Mild to moderate symptoms: Sneezing, itchy or watery eyes, runny or stuffy nose, rash, itching.
- Severe symptoms: Difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat, anaphylaxis (a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment).
Common skin allergy symptoms:
Hives (Urticaria)
- Description: Raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape.
- Appearance: Often red or skin-colored, may change location and appearance.
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Description: Chronic condition causing inflamed, itchy skin.
- Appearance: Dry, scaly patches that can be red or dark, often on the face, elbows, or knees.
Contact Dermatitis
- Description: Skin reaction due to contact with an allergen or irritant.
- Appearance: Red, itchy rash, sometimes with swelling and blisters, localized to the area of contact.
Rashes
- Description: General term for irritated skin that may appear red, inflamed, or blistered.
- Appearance: Can vary from small patches to widespread areas, often itchy or painful.
Hives
- Description: Itchy, raised areas on the skin.
- Appearance: Can be red or pale, and may change size or location.
Swelling (Angioedema)
- Description: Deeper swelling, often around the eyes, lips, or hands.
- Appearance: Puffy, sometimes painful swelling that can last for hours to days.
Blisters
- Description: Fluid-filled bumps that can be caused by contact with allergens.
- Appearance: Small, fluid-filled sacs on the skin.
Flaking or Peeling Skin
- Description: Skin becomes dry and starts to peel.
- Appearance: Scaly patches or flakes, commonly seen in eczema or psoriasis.
Itching
- Description: Persistent itchiness of the skin.
- Appearance: Can be associated with various skin reactions and often accompanies other symptoms.
Diagnosis and Treatment
- 1. Avoidance
- Identify and Avoid Triggers: Minimize exposure to known allergens like pollen, pets, and certain foods.
- 2. Medications
- Antihistamines: Reduce sneezing and itching.
- Nasal Corticosteroids: Ease nasal congestion.
- Decongestants: Relieve nasal stuffiness.
- Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists: Manage allergic inflammation.
- Eye Drops: Treat itchy, red eyes.
- 3. Immunotherapy
- Allergy Shots: Gradually desensitize to allergens.
- Sublingual Tablets: Build tolerance to pollen allergens.
- 4. Emergency Treatment
- Epinephrine: Used for severe reactions (anaphylaxis).
- 5. Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Allergy-Proof Home: Use air purifiers, dehumidifiers, and hypoallergenic bedding.
- Saline Nasal Rinses: Clear allergens from nasal passages.
- Proper Pet Care: Regular grooming and cleaning.
- 6. Dietary Adjustments
- Avoid Problem Foods: Eliminate foods you’re allergic to.
- 7. Professional Help
- Allergists and Immunologists: For diagnosis and specialized treatment.
- 8. Education and Support
- Learn and Get Support: Understand your allergies and connect with support groups.
Diagnosis: Allergies can be diagnosed through medical history, skin tests, blood tests, or elimination diets (for food allergies).
Treatment: Avoiding known allergens, taking antihistamines, using nasal sprays, and in severe cases, carrying an epinephrine auto-injector for anaphylaxis.
Key Points:
- Genetics: Allergies often run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain allergens or pollutants can increase the risk of developing allergies.
- Immune System Overreaction: In individuals with allergies, the immune system mistakenly identifies harmless substances as threats, leading to allergic reactions.
If you suspect you have allergies, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.