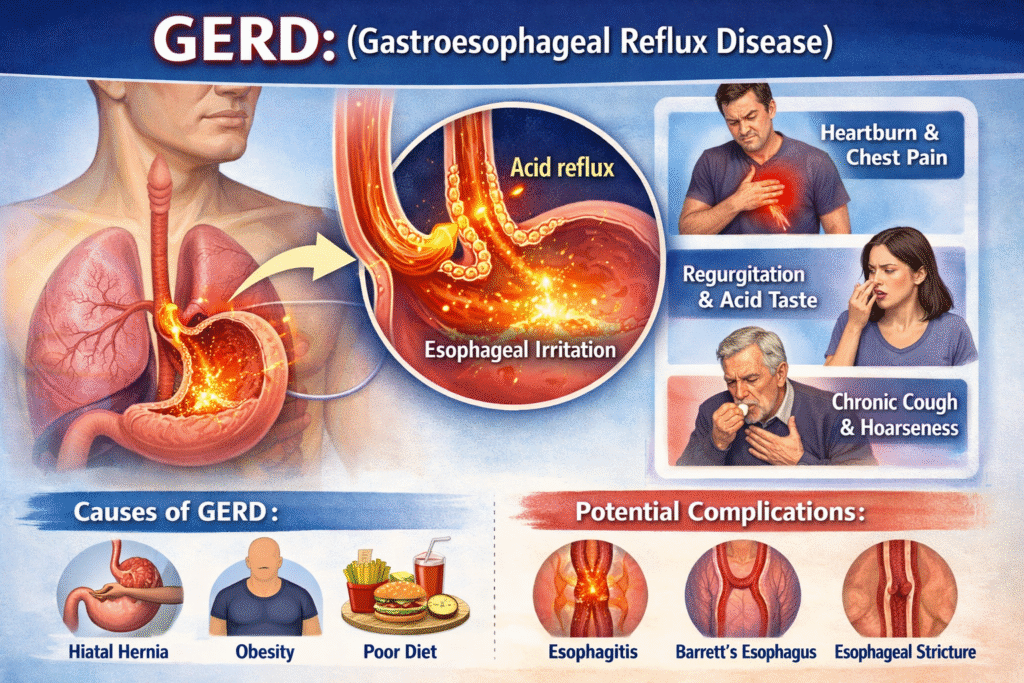
GERD:(Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
A Complete Guide to Optimal Digestive Health.
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease), commonly known as GERD, is a chronic digestive disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. This condition occurs when stomach acid or food contents frequently flow back into the esophagus (food pipe), causing irritation and discomfort. While occasional acid reflux is common, frequent occurrences may be a symptom of GERD and require medical attention.
What Is GERD?
GERD develops when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES)—a ring of muscle that acts as a valve between the stomach and esophagus—becomes weak or relaxes at the wrong time. This allows acidic stomach contents to move upward, leading to symptoms such as heartburn and regurgitation What Is GERD?
Common Symptoms of GERD
GERD symptoms can vary from mild to severe and may worsen after meals or while lying down. Common signs include:
- Burning sensation in the chest (heartburn)
- Sour or bitter taste in the mouth
- Acid regurgitation
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chronic cough or sore throat
- Hoarseness of voice
- Chest pain (sometimes mistaken for heart problems)
- Feeling of a lump in the throat
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing GERD, including:
- Obesity or excess body weight
- Eating large meals or eating late at night
- Fatty, spicy, or acidic foods
- Caffeine, chocolate, alcohol, and carbonated beverages
- Smoking
- Pregnancy
- Hiatal hernia
- Certain medications (pain relievers, blood pressure medications)
How GERD Is Diagnosed
Doctors may diagnose GERD based on symptoms and medical history. In some cases, additional tests are required, such as:
- Endoscopy to examine the esophagus
- pH monitoring to measure acid levels
- Esophageal manometry to assess muscle function
Treatment Options for GERD
1. Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
Simple daily habits can significantly reduce symptoms:
- Eat smaller, frequent meals
- Avoid lying down immediately after eating
- Elevate the head while sleeping
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Quit smoking
- Limit trigger foods and beverages
2. Medications
Doctors may recommend:
- Antacids for quick relief
- H2 blockers to reduce acid production
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) for healing the esophagus
3. Surgical Treatment
In severe or medication-resistant cases, surgery such as fundoplication may be considered to strengthen the LES.
Complications of Untreated GERD
If left untreated, GERD can lead to serious complications, including:
- Esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus)
- Esophageal strictures (narrowing)
- Barrett’s esophagus (increased cancer risk)
- Chronic respiratory issues
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical help if you experience symptoms more than twice a week, have difficulty swallowing, unexplained weight loss, or chest pain that mimics heart problems.
Living a Healthy Life with GERD
GERD is a manageable condition. With proper lifestyle changes, dietary control, and medical guidance, most people can live comfortably and prevent long-term complications. Listening to your body and addressing symptoms early plays a key role in maintaining good digestive health.
Everything You Need to Know About Hair Loss?
Need To Know More About GERD
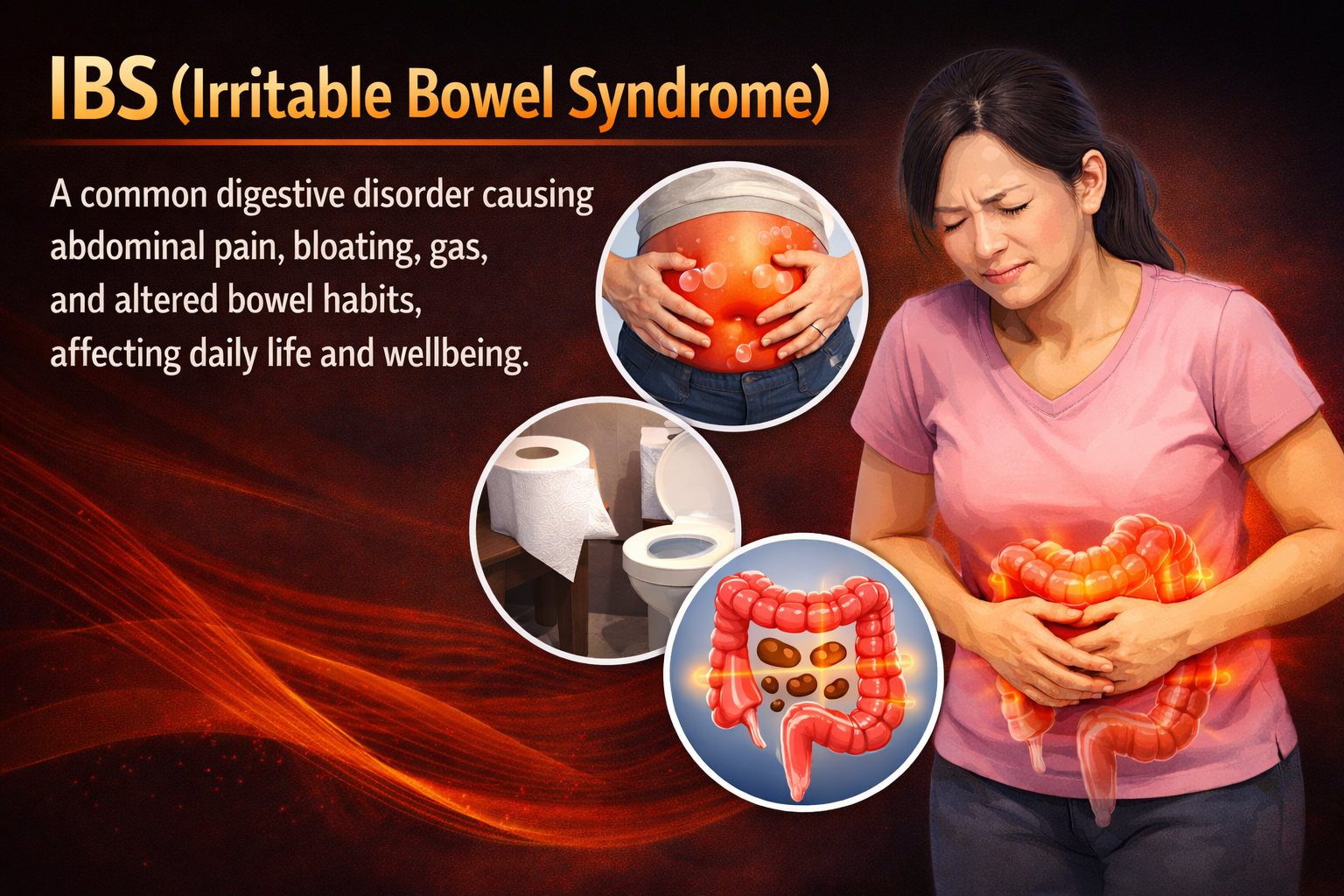
IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome): Causes, Symptoms, Types, Diet, and Effective Management IBS (Irritab…
GERD: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
GERD:(Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) A Complete Guide to Optimal Digestive Health. GERD (Gastroeso…
Hair Loss: Everything You Need to Know About Hair Loss?
Hair loss is a common concern affecting millions of men and women worldwide. While losing a few stra…
Migraine
What you need to know about Migraine? Migraine is a type of headache that can cause intense pain, of…
Everything you need to know about Vitamin D Deficiency?
Vitamin D Deficiency Vitamin D deficiency occurs when your body doesn’t have enough of this essentia…