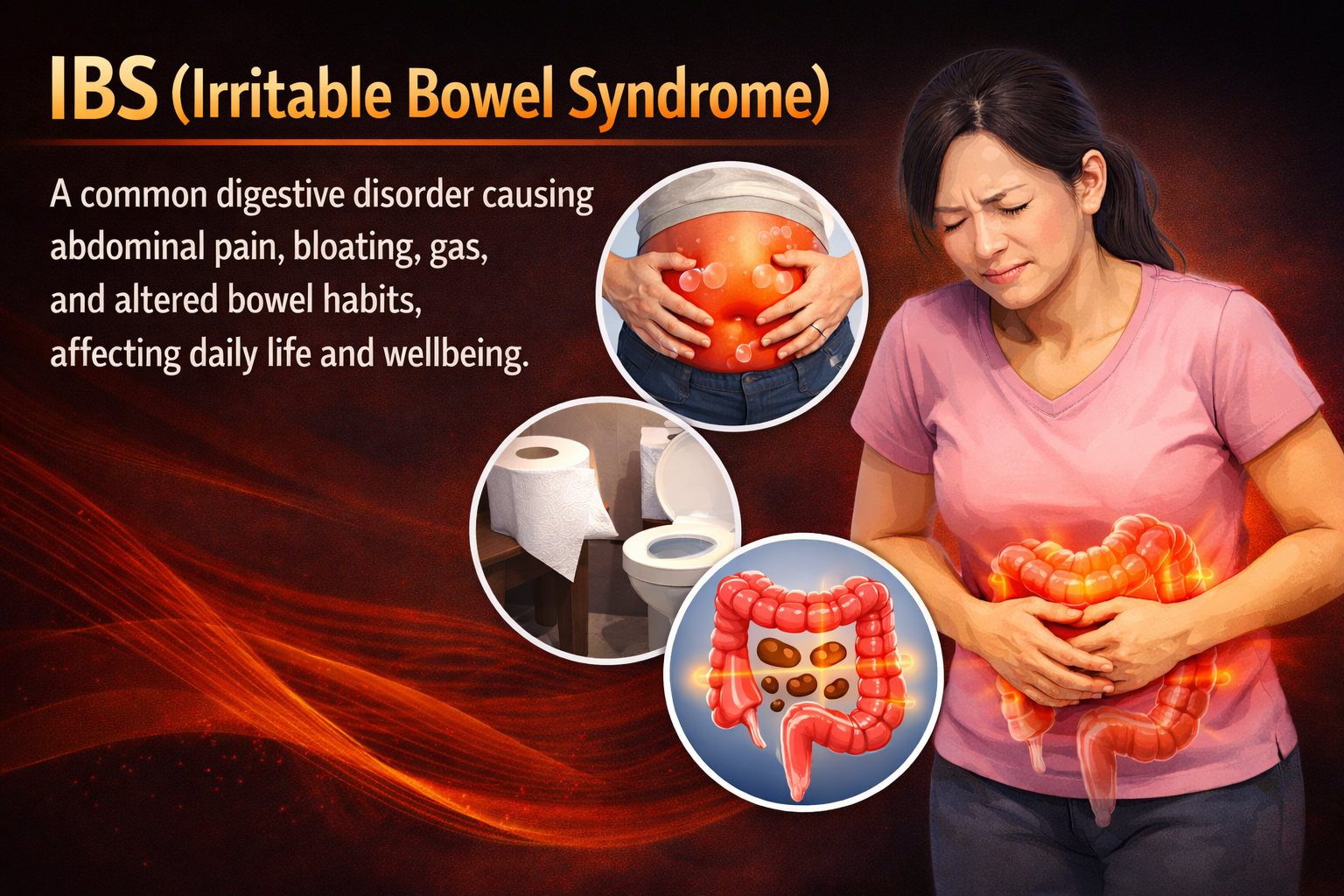
What is Hypertension?
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, happens when the blood pushes too hard against the walls of your arteries every time. We measure blood pressure using two numbers: one shows the pressure when your heart beats (systolic), and the other shows the pressure when your heart is resting between beats (diastolic).
Hypertension frequently has no symptoms, which is why it’s sometimes called the “silent killer.” If not addressed, it can cause significant health problems, issues such as heart disease, stroke, kidney damage, and vision loss.
Here is a quick review:
- Normal Blood Pressure: Typically, a normal reading is around 120/80 mm Hg.
- Elevated Blood Pressure: Readings between 120-129 systolic and less than 80 diastolic are considered elevated, indicating a higher risk of developing hypertension.
- Hypertension Stage 1: Blood pressure ranging from 130-139 systolic or 80-89 diastolic.
- Hypertension Stage 2: Blood pressure of 140/90 mm Hg or higher.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure common causes:
- Genetics: Family history of high blood pressure can increase your risk.
- Age: Blood pressure usually to rise with age.
- Obesity: Being overweight can put pressure on the heart and increase blood pressure.
- Diet: High salt (sodium) intake, low potassium, and poor diet can contribute to hypertension.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise can lead to weight gain and higher blood pressure.
- Alcohol and Smoking: Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking can raise blood pressure.
- Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to higher blood pressure over time.
- Chronic Conditions: Certain diseases like kidney disease or hormonal disorders can cause secondary hypertension.
Treatment for hypertension :
Lifestyle Changes:
- Diet:
- Reduce Salt Intake: Lowering sodium helps reduce blood pressure.
- Eat Healthy Foods: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Limit Alcohol: Drink in moderation or avoid it.
- Reduce Caffeine: Cut back on caffeinated beverages.
- Exercise:
- Stay Active: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, like walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Lose Excess Weight: Even a small amount of weight loss can help reduce blood pressure.
- Quit Smoking:
- Avoid Tobacco: Smoking can raise blood pressure and harm overall heart health.
- Manage Stress:
- Relaxation Techniques: Practice methods like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga.
- Monitor Blood Pressure:
- Regular Check-Ups: Keep track of your blood pressure at home and see your doctor regularly.
Medications:
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, doctors may prescribe medications. Common types include:
- Diuretics: Help the body get rid of excess sodium and fluid.
- ACE Inhibitors: Relax blood vessels by blocking a substance that narrows them.
- Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs): Help relax blood vessels by blocking the action of a substance that causes constriction.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Prevent calcium from entering heart and blood vessel cells, leading to relaxed vessels.
- Beta-Blockers: Reduce the workload on the heart by blocking the effects of adrenaline.
Avoid self-medicating—always consult your doctor before starting or changing any medication.