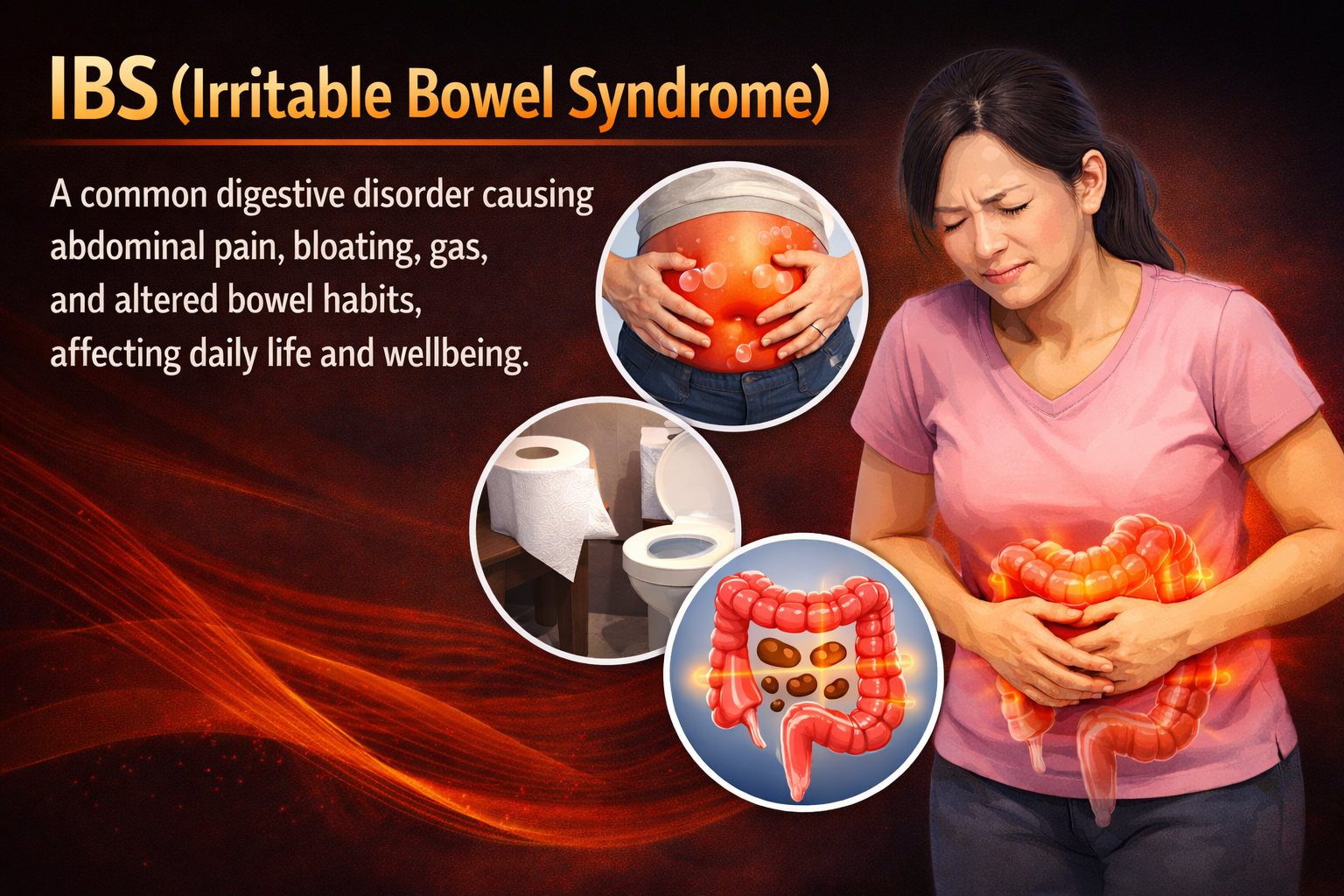
Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency occurs when your body doesn’t have enough of this essential nutrient. It plays a key role in helping your body absorb calcium, which is vital for strong bones and healthy teeth. Without enough vitamin D, your bones can become weak, and you might have pain or muscle weakness.
Vitamin D deficiency happens when your body doesn’t have enough vitamin D. This vitamin is crucial for several reasons:
- Bone Health: Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium, which is essential for strong bones and teeth. However, without enough vitamin D, bones can gradually become brittle or even misshapen.
- Immune Function: It plays a role in keeping your immune system healthy, which helps your body fight off infections.
- Muscle Function: Adequate vitamin D helps maintain muscle strength and function.
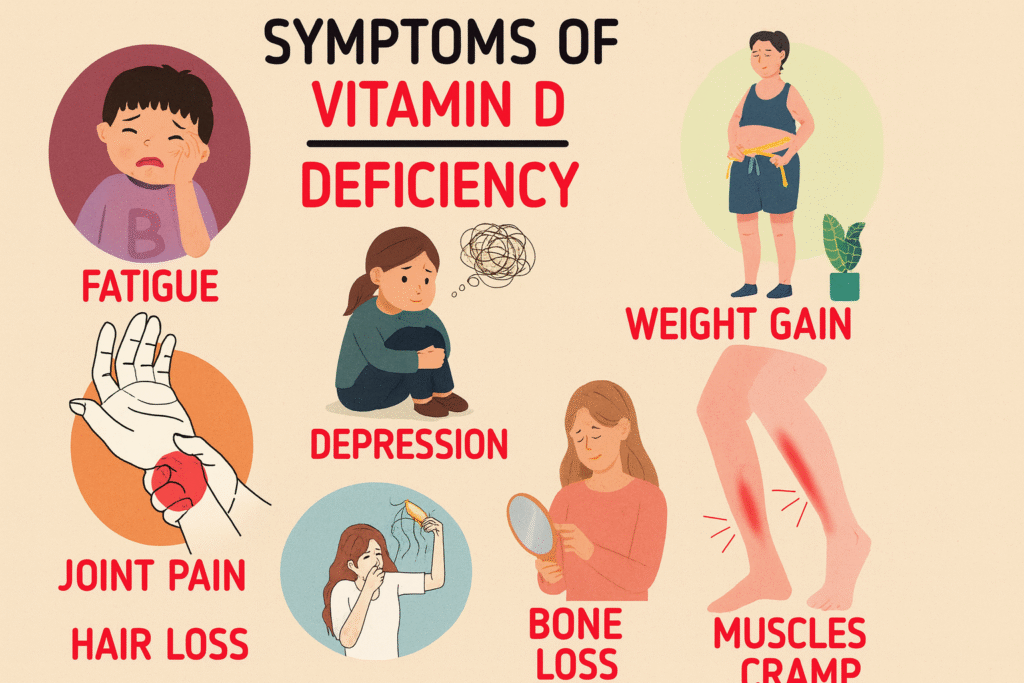
Common symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency:
- Mood Changes: In some cases, it may affect your mood and contribute to conditions like depression.
- Bone Pain and Weakness: As a result, you might experience aches in your bones or feel weak, especially in your legs, arms, or back.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or low in energy.
- Muscle Weakness: Difficulty with muscle strength or coordination.
Causes of Vitamin D Deficiency:
- Lack of Sunlight: Vitamin D is produced in the skin in response to sunlight. If you don’t get enough sun exposure, you might be at risk.
- Diet: Not eating enough foods rich in vitamin D (like fatty fish, fortified milk, and eggs).
- Medical Conditions: Certain health issues can affect how your body processes vitamin D.
Prevention and treatments:
- Sunlight Exposure:
- Duration: Aim for about 10–30 minutes of sunlight exposure a few times a week; however, the exact duration varies depending on factors such as skin type, location, and season.
- Safe Sun Practices: Use sunscreen and avoid peak sun hours to reduce the risk of skin damage while still getting some vitamin D.
- Diet:
- Vitamin D-Rich Foods: Include foods like:
- Fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Fortified foods (e.g., fortified milk, orange juice, cereals)
- Egg yolks
- Liver
- Fortified Foods: Many countries fortify certain foods with vitamin D, so consuming these can help boost your intake.
- Vitamin D-Rich Foods: Include foods like:
- Supplements:
- Vitamin D Supplements: These can help if you’re not getting enough from sunlight or diet. Common forms include vitamin D2 and vitamin D3. D3 is usually preferred because it’s more effective at raising vitamin D levels in the blood.
- Dosage: Follow your doctor’s recommendations for dosage, as too much vitamin D can also have health risks.
- Address Underlying Conditions:
- Health Conditions: Some medical conditions can affect vitamin D metabolism (like celiac disease or Crohn’s disease). Managing these conditions with the help of a Doctor can help improve vitamin D levels.