What you need to know about Migraine?

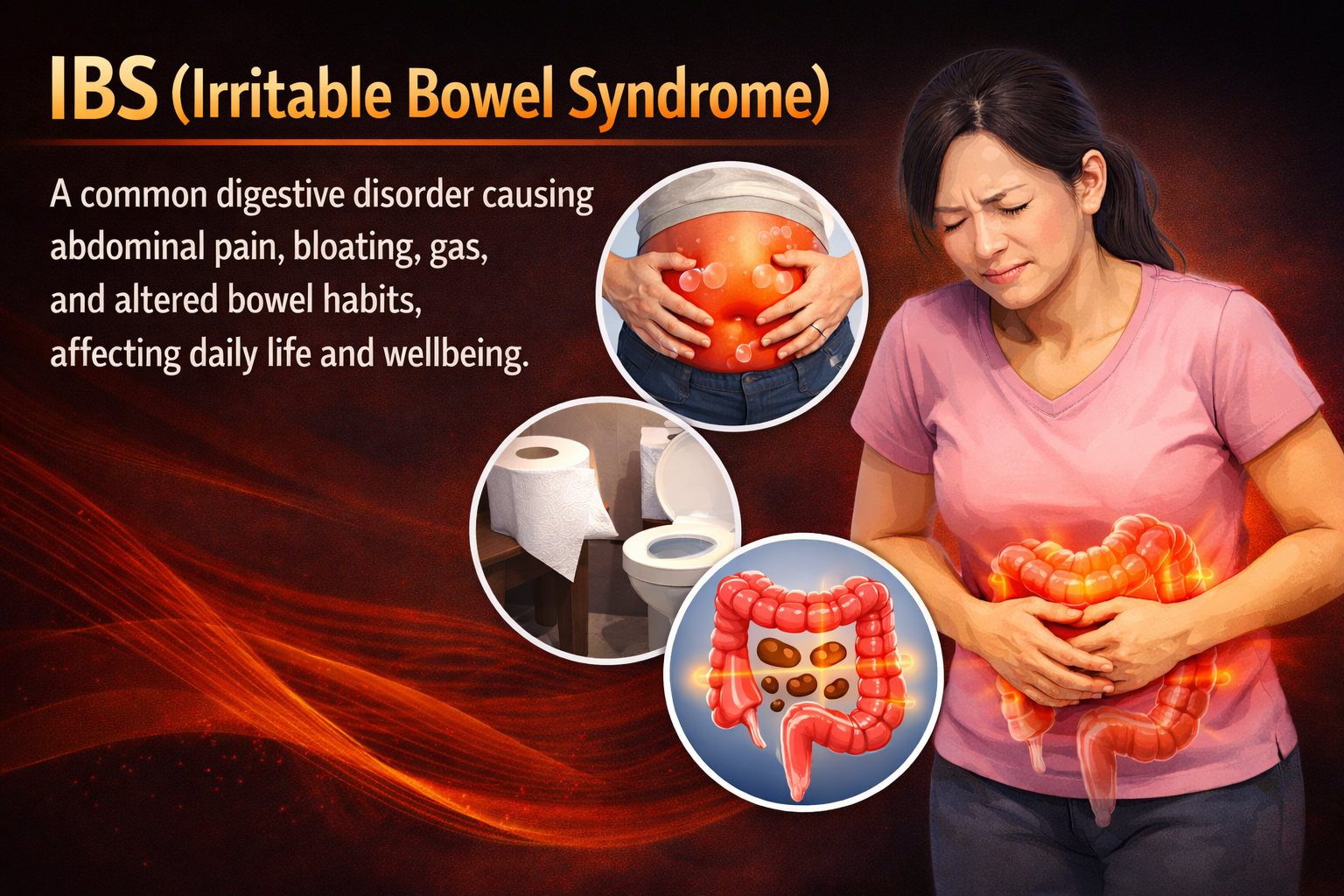
Migraine is a type of headache that can cause intense pain, often on one side of the head. It may come with nausea, sensitivity to light or sound, and sometimes even blurry vision. People with migraines might need to rest in a quiet, dark room until the pain goes away.
Common symptoms of migraine include:
- Intense throbbing or pulsing pain, often on one side of the head.
- Tingling or numbness in the face or extremities.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Sensitivity to light, sound, or even smells.
- Blurred vision or visual disturbances.
Types of Migraine
There are different types of migraines, the most common being:
- Migraine without Aura – Sudden headache without warning signs.
- Migraine with Aura – Visual or sensory disturbances before pain.
- Chronic Migraine – Headaches on 15 or more days per month.
- Hemiplegic Migraine – Rare type causing temporary weakness on one side of the body.
- Vestibular Migraine – Mostly causes dizziness or balance issues.
The exact causes aren’t understood, but some common triggers include:
- Genetics: Migraines often run in families, suggesting a genetic component.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in estrogen levels, especially in women, can trigger migraines.
- Triggers: Certain foods (like aged cheeses or processed meats), stress, lack of sleep, and environmental factors (like bright lights or strong smells) can trigger migraines in susceptible individuals.
- Neurological factors: Changes in brain chemicals (neurotransmitters) and nerve pathways may play a role in initiating migraines.
- Physical factors: Physical exertion, changes in weather, and certain medications can also contribute to migraine onset.
Here are some home treatments that may help relieve migraine symptoms:
- Avoid triggers: Identify and avoid triggers such as certain foods, strong smells, or bright lights.
- Rest in a quiet, dark room: Lie down in a calm environment and try to relax.
- Apply a cold or warm compress: Place a cold pack or a warm cloth on your forehead or neck to help alleviate pain.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water, as dehydration can sometimes trigger migraines.
- Try over-the-counter pain relievers: Ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce migraine pain if taken early enough.
- Massage: Gently massage your temples, neck, or shoulders to help relax tense muscles.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga can help reduce stress, which can be a migraine trigger.
Treatment and Management for Migraine
Although migraines cannot be cured completely, they can be effectively managed with proper care. Treatments include:
Medications
- Pain-relieving medicines (NSAIDs, triptans)
- Preventive drugs for frequent migraines
- Anti-nausea medications
Lifestyle Changes
- Maintaining proper sleep patterns
- Eating meals on time
- Staying hydrated
- Managing stress through yoga, meditation, or deep breathing
- Avoiding known triggers
Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture
- Massage therapy
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Vitamin and mineral supplements (after consulting a doctor)
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if:
- Migraines become more frequent or severe
- Symptoms change suddenly
- Headache starts after a head injury
- You experience weakness, confusion, or difficulty speaking