Melatonin: Benefits, Uses, Dosage, and Side Effects
What is Melatonin?
Melatonin is a natural hormone produced by the pineal gland in the brain. It plays an important role in regulating the body’s sleep-wake cycle (circadian rhythm). Known as the “sleep hormone,” melatonin helps signal the body when it’s time to rest. Although it’s produced naturally, it is also available in supplement form, which is commonly used to treat sleep disorders.
How Melatonin Works
The body’s production of melatonin increases as it gets darker in the evening and decreases with exposure to light in the morning. This hormonal signal prepares the body for sleep. Supplements mimic this natural process, making it easier for individuals to fall asleep, especially in the following cases:
- Insomnia
- Jet lag
- Shift work sleep disorder
- Delayed sleep phase syndrome
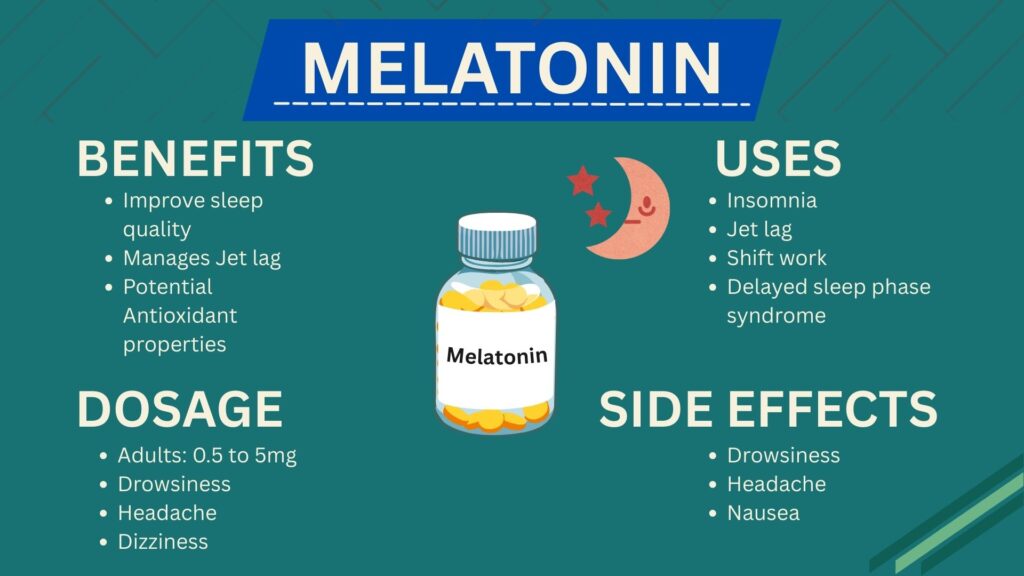
Benefits of Melatonin
- Improves sleep quality – helps reduce the time it takes to fall asleep and increases overall restfulness.
- Manages jet lag – helps reset the body clock when traveling across time zones.
- Supports shift workers – helps those with irregular work schedules align their sleep cycles.
- Potential antioxidant properties – some studies show that melatonin may protect cells from damage.
- May support eye health – research links melatonin to better retinal health due to its antioxidant effects.
Recommended Dosage
- Adults: Usually 0.5 to 5 mg taken 30-60 minutes before bedtime.
- Children: Should only be used under medical supervision.
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting supplements, as dosage needs vary.
Possible side effects
Melatonin is generally considered safe for short-term use, but some people may experience:
- Daytime drowsiness
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Mood swings (rare)
- Who should avoid melatonin?
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women (unless prescribed by a doctor)
- People taking blood thinners, diabetes medications, or immunosuppressants
- People with depression or seizure disorders should consult a doctor before use.
Natural ways to increase melatonin
- Minimize screen time before bed (blue light reduces its production)
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule
- Create a dark, cool sleep environment
- Eat foods like (cherries, bananas, oats, nuts)
- Bottom line
Melatonin can be a powerful aid in improving sleep and managing circadian rhythm disruption. Although it is widely available and generally safe, it should be used thoughtfully and ideally under medical guidance. Combining melatonin supplements with healthy sleep habits provides the best results for long-term rest and wellness.