Breast Cancer: A type of cancer that forms in the cells of the breast. It can develop in various parts of the breast, including the milk ducts (ductal carcinoma) and milk-producing glands (lobular carcinoma).
Types of Breast Cancer
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC): The most common type, starting in the milk ducts and spreading to nearby tissues.
- Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC): Originates in the lobules (milk-producing glands) and spreads to surrounding tissues.
- Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS): A non-invasive cancer where abnormal cells are found in the ducts but haven’t spread to surrounding tissue.
- Lobular Carcinoma In Situ (LCIS): Abnormal cells are found in the lobules, but it is not considered a true breast cancer. It frequently indicates an increased risk of developing breast cancer in the future.
- Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Lacks estrogen receptors, progesterone receptors, and excess HER2 protein. It is more aggressive and has fewer treatment options.
- HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: The cancer cells have an excess of HER2 protein, which promotes the growth of cells.
- Inflammatory Breast Cancer: A rare and aggressive form where cancer cells block lymph vessels in the skin of the breast, causing it to become red, swollen, and warm.
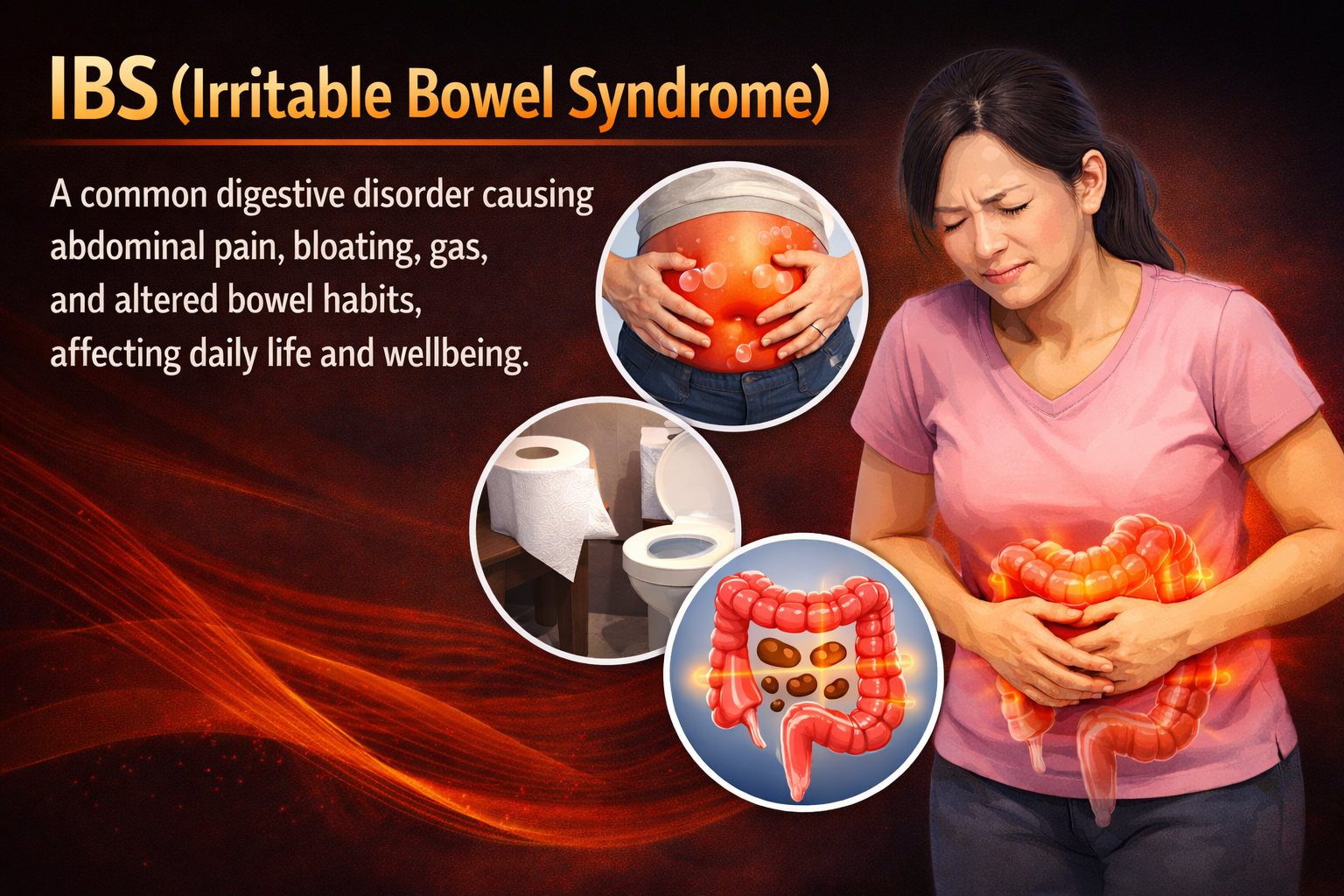
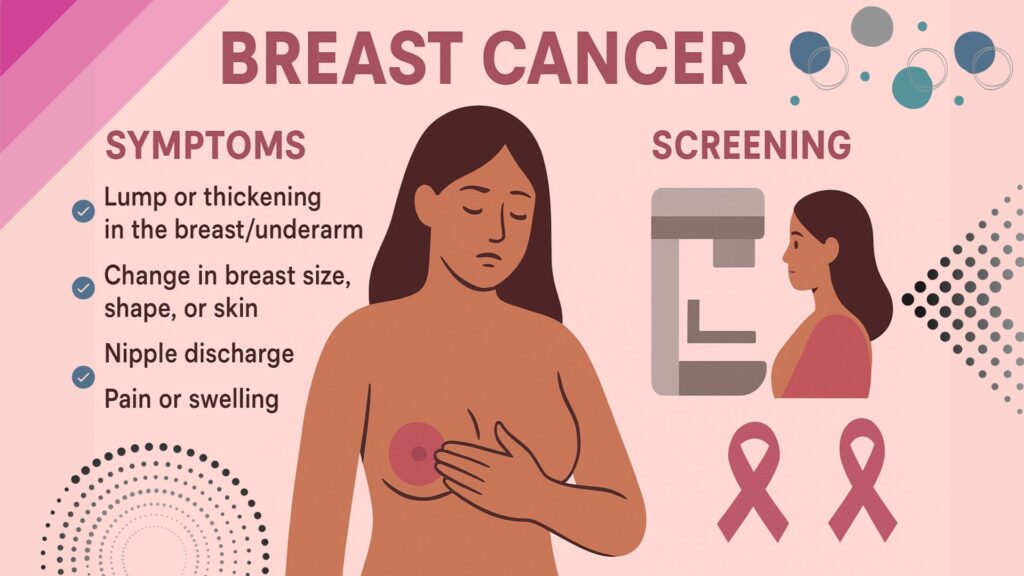
Symptoms of Breast Cancer:
Symptoms can vary but may include:
- A lump or mass in the breast or underarm area.
- Changes in the size or shape of the breast.
- Changes in the skin or nipple, such as dimpling, redness, or scaling.
- Discharge from the nipple, which may be blood-stained or clear fluid.
- Persistent pain in the breast or nipple.
Risk Factors
Several factors may increase the risk of developing breast cancer, including:
- Gender: Women are at higher risk.
- Age: Risk increases with age.
- Family History: Having close relatives with breast cancer, especially at a young age.
- Genetics: Mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2.
- Hormonal Factors: Early menstruation, late menopause, or hormone replacement therapy.
- Lifestyle: Alcohol consumption, obesity, and lack of physical activity.
- Radiation Exposure: Previous radiation treatments, particularly to the chest area.
Diagnosis
It is typically diagnosed through:
- Mammography: An X-ray of the breast used for screening and detecting abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the breast and can help distinguish between solid masses and fluid-filled cysts.
- Biopsy: Removal and examination of breast tissue to determine if cancer cells are present.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images and may be used for further evaluation.
Treatment
Treatment options vary based on the type, stage, and other individual factors and may include:
- Surgery: Options include lumpectomy (removal of the tumor and a small amount of surrounding tissue) or mastectomy (removal of one or both breasts).
- Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy waves to target and kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
- Hormone Therapy: Blocks or removes hormones that fuel cancer growth, such as estrogen.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific characteristics of cancer cells, such as HER2-positive cancers.
- Immunotherapy: Uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Prognosis
The prognosis for breast cancer depends on factors like the stage at diagnosis, the type of cancer, and how well it responds to treatment. Early detection often leads to better outcomes. Regular screening and self-exams are crucial for early detection and successful treatment.
Prevention
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent it, the following measures can help reduce risk:
- Regular Screenings: Mammograms and clinical breast exams.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, limiting alcohol, and a balanced diet.
- Genetic Testing: For those with a family history or genetic predisposition, genetic testing and preventive measures (like prophylactic mastectomy) may be considered.
Understanding breast cancer and its various aspects can help in early detection and effective management.